
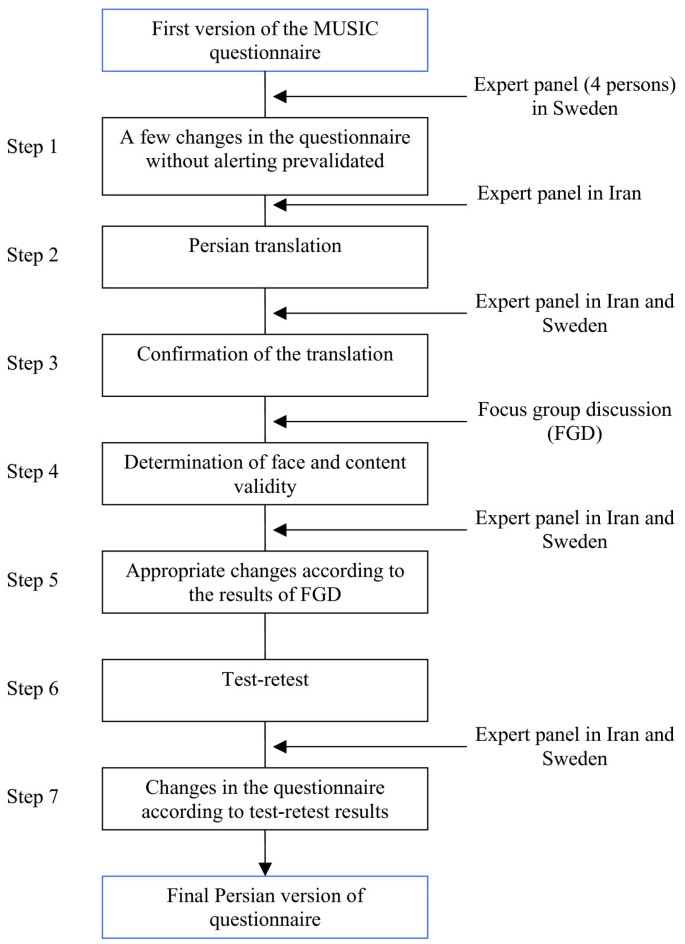
Researchers have developed a variety of evaluation tools for testing the effect of interventions. However, these factors are most significant for people with enhanced LDL-C levels. All adults should be encouraged to adopt a healthy diet. These dietary changes can decrease LDL-C, triglycerides, body weight, and so forth. Dietary changes include those that limit total cholesterol, fat, saturated fat, and energy, with the inclusion of two grams of plant stanols/sterols every day and enhanced consumption of soluble fiber. Several research studies have shown the efficacy of lifestyle interventions and dietary changes in decreasing LDL-C and cardiovascular issues. Īs per recommendations, the primary therapy for hypercholesterolemia specifies lifestyle and dietary modifications. The majority of lipid disorders (80%) are associated with lifestyles and diet, despite the significant role of familial disorders (20%). Dyslipidemias can be generally divided into low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), atherogenic dyslipidemia, hypertriglyceridemia, mixed lipid disorders, and excess lipoprotein(a). Īs an extensive term, dyslipidemia refers to a range of lipid disorders. Forecasts suggest that in China, as the population increases and becomes generally older, the incidence of CVD will increase by over 50% in the following 20 years. Although CVD deaths are decreasing in the developed world, they continue to rise in developing countries. IntroductionĪs a modifiable and independent risk factor, dyslipidemia plays a causal role in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease (CVD), which now is the main cause of death in the world. It is suitable for providing scientific assessments for targeted health education interventions. The DDKQ is a reliable and valid measure of dyslipidemia dietary knowledge. The questionnaire was also able to distinguish between participants with/without a medical background medical workers produced significantly higher total scores (16.70☒.84 vs. The mean item difficulty (P) was 0.55 and ranged from 0.15 to 0.83, and the mean item discrimination index (D) was 0.36, ranging from 0.21 to 0.58. It demonstrated adequate content validity (0.94), face validity, internal consistency (KR20 = 0.67), and test-retest reliability (0.74). The DDKQ consisted of 5 parts, with 25 items in total. Two Delphi rounds were performed to ensure content validity and face validity, items were pretested and filtered through item analysis, and the reliability and validity of the final questionnaire were checked.

The initial, multiple-choice dyslipidemia dietary knowledge questionnaire (DDKQ) was formed based on a literature review of previous studies. This study developed a questionnaire to test dyslipidemia dietary knowledge. Adequate knowledge of the correct diet for dyslipidemia is an effective preventive strategy against cardiovascular disease. Diet and lifestyle interventions positively contribute to the management of dyslipidemia. Dyslipidemia is one of the most important modifiable risk factors for cardiovascular disease.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
